Blockchain – Why Bitcoin Works
Welcome back, I’m Kathleen Bitcoin. I’m 20 years old, new to the bitcoin world, and here to write on the current hot topics in bitcoin while I learn about it along the way.
So, all this talk about the blockchain, but what is it really? We know the basics, but let’s dive deeper.
Blockchain
The blockchain is different from a typical database because of “the way the data is structured. A blockchain collects information together in groups, also known as blocks, that hold sets of information. Blocks have certain storage capacities and, when filled, are chained onto the previously filled block, forming a chain of data known as the ‘blockchain’. All new information that follows that freshly added block is compiled into a newly formed block that will then also be added to the chain once filled” (Conway, Luke. “Blockchain Explained.” Investopedia, Investopedia, 17 Nov. 2020, www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp). Using this system makes an irreversible timeline of data. When a block is filled it is set in stone and becomes a part of said timeline. Each block in the chain is given an exact timestamp when it is added to the chain.
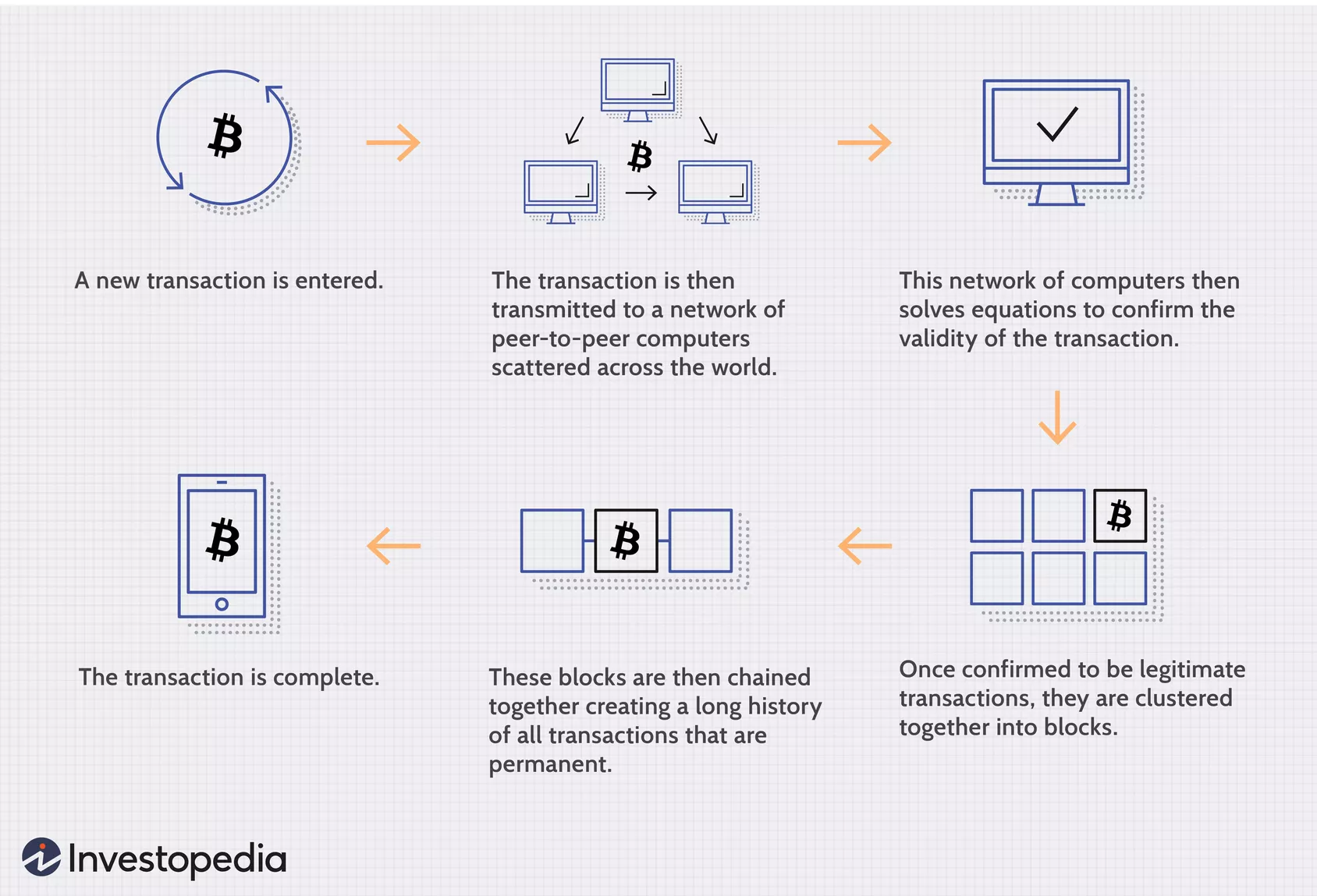
In a blockchain, each node, or computer, has a full record of the data that’s been stored on it since it was formed. With bitcoin, the data is an entire history of all of its transactions, ever. If one computer has an error, it can use any and all of other nodes to correct itself. This way, no one node can change information held within it. Because of this, the transaction history in each block that makes up bitcoin’s blockchain is irreversible. In this case, if someone attempted to tamper with the transaction history in any way, the blockchain would just use the other nodes to correct itself!
Decentralization
If we’re going to talk about the blockchain, we need to talk about its decentralization. With any old database, it can all be done on a group of computers under one roof, but when it comes to bitcoin, it takes several and they are all operated by separate individuals; which is why it’s decentralized, because it’s not controlled by any one person. This is great, because it offers every single user an opportunity to become one of the network’s many payment processors.
Pros and Cons
Let’s talk Pros and Cons. Pros first: More accuracy by relying on computers to do the work; decentralization stops tampering; transactions are secure and efficient. The list could go on. Now onto cons: higher technology cost from mining; low transactions per second, In all honesty, the pros clearly outweigh the cons to using a blockchain as a way of tracking bitcoin transactions.
If you want to start Dollar Cost Averaging your way into buying bitcoin, use our link and start your plan today to get $10 of free bitcoin dropped into your account: https://www.swanbitcoin.com/CypherSafe
And don’t forget to protect it with a CypherWheel!
Thanks again,
Kathleen Bitcoin
Twitter: @KathleenBitcoin








